Mastering Google Ads Pricing in 2025: A Comprehensive Guide for Advertisers

Are you ready to take your Google Ads campaigns to the next level and maximize your advertising budget?
Let our team of experts guide you through the complexities of Google Ads pricing and strategy.
The Google Ads pricing landscape evolves dynamically, driven by factors such as technological advancements and changes in user behavior. By 2025, advertisers can expect a more complex, data-driven environment. Mastery will require understanding the underlying factors influencing ad costs, adopting effective bidding strategies, and leveraging the expertise of Google Ads professionals.
Table of Contents
How Much Does Google Advertising Cost?
Google advertising cost is not a one-size-fits-all as it varies based on several factors. These factors include the competition for keywords, quality of ads, and the targeted demographics. While some businesses may spend thousands of dollars on Google Ads, others may only need to spend a few hundred.
- CPC: The average cost per click (CPC) on a Google ad in 2025 is projected to range between $1.00 and $2.00, depending on the industry and the competitiveness of the keywords.
- CPM: The cost per mille (CPM), or the expense to reach 1,000 people with your ad, is anticipated to fluctuate between $2.00 and $5.00.
- Monthly Advertising Budget: Most advertisers are expected to allocate a monthly budget of $500 to $2000 for their Google ads, with variations based on the scale and nature of their businesses.
- Factors Influencing Cost: Several factors influence the cost of Google ads, including the competition for keywords, quality of the ad content, geographical targeting, time of the day, and the bidding strategy implemented.
- Minimum Budget: Google suggests a daily budget based on businesses' goals and the average cost of ads in their industry. There isn't a minimum ad spend, but a higher budget allows for more visibility and reach.
- Ad Management Costs: Ad management costs, typically ranging from 12% to 30% of the total ad spend, should also be factored into the budget. These include costs for ad creation, campaign setup, and ongoing optimization.
- ROAS: The return on ad spend (ROAS) differs across industries. For instance, e-commerce businesses may see a higher ROAS due to their direct response nature, while service-based industries might have a longer sales cycle and lower ROAS.
- Scaling Your Ads: Once a successful strategy is identified, consider gradually increasing your daily budget (around 15-25% per week) and refining your targeting to concentrate on the most efficient ad formats and audiences. This will help maximize your ad performance and improve your ROAS.
Principal Factors Influencing Google Ads Costs
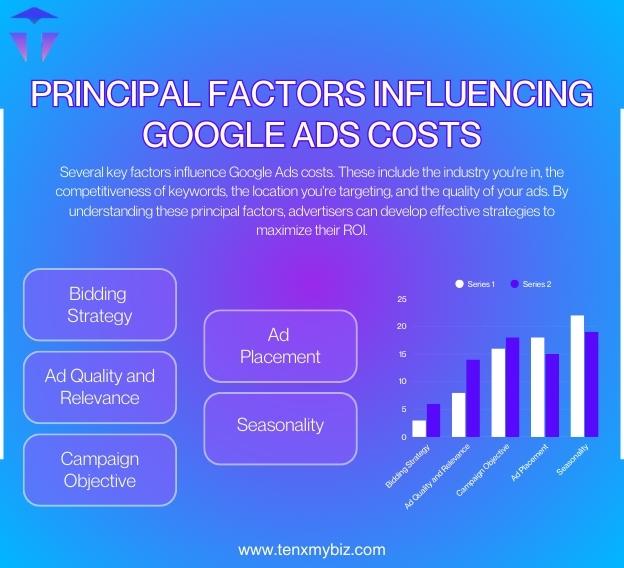
Several key factors influence Google Ads costs. These include the industry you're in, the competitiveness of keywords, the location you're targeting, and the quality of your ads. By understanding these principal factors, advertisers can develop effective strategies to maximize their ROI.
Bidding Strategy
- Automated Bidding: Google's smart algorithms will bid for you, aiming to achieve your campaign goals (such as clicks or conversions) within your allotted budget.
- Manual CPC Bidding: You retain more control by setting a maximum amount that you could pay for each click on your ad.
Enhanced CPC Bidding: Google adjusts your bids to maximize conversions within your budget.
- Target Audience Specificity: Narrower target audiences can increase the likelihood of reaching potential customers, potentially reducing costs.
- Location Targeting: Geographical targeting can influence costs, with certain locations being more expensive due to high demand or competition.
- Keyword Competition: The competitiveness of your chosen keywords can significantly impact costs. High demand keywords are more expensive to bid on.
Ad Quality and Relevance
- Quality Score: Google rates your ads based on their relevance to the search terms, the quality of your landing page, and your ad's click-through rate (CTR).
- CTR: Ads with higher CTRs are considered more relevant and can lead to lower costs.
- Ad Copy: Well-written ad copy that resonates with your target audience can increase engagement and lower costs.
- Ad Extensions: Use of ad extensions can improve your ad's visibility and click-through rate, potentially reducing costs.
Campaign Objective
- Brand Awareness: Campaigns aiming to increase brand visibility may have different cost structures than those focused on conversions.
- Website Traffic: If your goal is to drive traffic to your website, you might need to bid higher to compete effectively.
- Conversions: Campaigns aiming to increase sales or other conversions may require higher bids to reach the right audience.
Seasonality
- Holidays and Special Events: Ad costs can rise during peak seasons or holidays due to increased competition.
- Industry Trends: Specific industries may see increased demand for ads at certain times of the year, affecting costs.
- Industry Competition: Highly competitive industries may face higher ad costs due to increased competition for the same target audience.
Ad Placement
- Search Network: Ads on Google's search network can be more expensive due to their high visibility and potential reach.
- Display Network: Ads on the display network (websites, apps, or videos) may be cheaper but can reach a wider audience.
Other Factors
- Device Targeting: The type of device you're targeting (mobile, desktop, tablet) can influence ad costs.
- Dayparting: Costs can vary throughout the day, with peak hours usually costing more.
- Budget: The amount you're willing to spend on your ads will ultimately determine your bid amounts and the number of impressions or clicks you can achieve.
Detailed Analysis of Google Ad Costs Across Different Industries
Google Ad costs vary significantly across different industries. For instance, industries with high customer lifetime values like legal services or insurance often have higher CPCs compared to other industries. This section will provide a detailed analysis of Google Ad costs across various industries, helping advertisers set realistic budget expectations.
| Industry | Avg Cost-Per-Click (CPC) | Avg Conversion Rate | Avg Cost-Per-Acquisition (CPA) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Legal Services | $6.75 | 6.98% | $96.69 |
| Insurance | $17.55 | 7.19% | $244.11 |
| Real Estate | $2.37 | 4.57% | $51.88 |
| Health & Medical | $2.62 | 5.58% | $47.04 |
| Retail | $1.35 | 2.50% | $54.00 |
| Education | $2.40 | 7.04% | $34.09 |
| Home Services | $2.94 | 5.68% | $51.75 |
| E-commerce | $1.16 | 1.91% | $60.75 |
| Finance | $3.72 | 5.12% | $72.63 |
| Technology | $3.80 | 2.98% | $127.37 |
Note: The above data is based on the global average.
Key Insights:
- Legal services and insurance industries have the highest CPC, primarily due to the high customer lifetime values they possess.
- E-commerce has a relatively low CPC but also a low conversion rate, leading to a higher CPA than industries with comparable CPC like retail or home services.
- Education industry has a moderate CPC but the highest conversion rate which results in the lowest CPA among all industries. Therefore, even with a smaller budget, advertisers in this industry can still achieve effective results.
- Technology industry has a high CPC but a lower conversion rate, leading to the highest CPA among all industries. This suggests that advertisers in this industry need to optimize their Ad campaigns for conversions to reduce the CPA.
Remember that these are average figures, and the actual cost can significantly vary based on the quality score, bid strategy, geographic location, and time of the year. Therefore, advertisers should regularly monitor and optimize their Google Ad campaigns to achieve the best results.
Is There a Prescribed Minimum Expenditure for Google Ads?
There's no prescribed minimum expenditure for Google Ads. You can start with any budget that suits your business needs. However, it's important to note that a lower budget may limit your ads' visibility and reach.
When considering Google Ads, businesses often wonder about budget allocation and how it impacts campaign performance. While there is no prescribed minimum expenditure, understanding various budget levels can help optimize your ad strategy. Below is a table that outlines potential budget ranges, their implications on visibility, reach, and expected outcomes.
Google Ads Budget Allocation Overview
| Budget Range | Visibility & Reach | Expected Outcomes | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| $1 - $10 per day | Very limited visibility; ads may only show on rare occasions. | Minimal clicks; may not generate significant leads. | Small businesses or testing new campaigns. |
| $10 - $50 per day | Moderate visibility; ads can appear in more searches. | Some clicks and potential leads, but still limited. | Startups or local businesses with niche offerings. |
| $50 - $200 per day | Good visibility; ads can reach a broader audience. | Increased clicks and lead generation; moderate ROI. | Established businesses looking to expand online. |
| $200 - $500 per day | High visibility; ads appear frequently in competitive searches. | Strong lead generation; better chance for conversions. | Mid-sized businesses or those in competitive sectors. |
| $500+ per day | Maximum visibility; ads dominate searches and display networks. | High volume of clicks and conversions; optimized ROI. | Large enterprises or aggressive market entrants. |
Key Considerations
- Ad Auction System: Google Ads operates on a bidding system. Higher budgets can lead to better ad placements, but it's also crucial to consider ad quality and relevance.
- Industry Standards: Different industries have varying average CPC (cost-per-click) rates. Researching your industry can help set realistic budget expectations.
- Testing and Iteration: Starting with a lower budget can be a good strategy for testing ad effectiveness. Gradually increase your budget based on performance metrics.
- Geographic Targeting: Your budget might need to be adjusted based on the geographic areas you are targeting, as competition levels can vary significantly.
- Campaign Goals: Align your budget with your overall marketing goals. A higher budget may be necessary for campaigns focused on brand awareness, while lower budgets may suffice for direct response campaigns.
While there is no set minimum expenditure for Google Ads, understanding how different budget levels impact visibility, reach, and expected outcomes is crucial for crafting an effective ad strategy. Businesses should evaluate their specific needs, industry dynamics, and marketing goals when setting their Google Ads budget.
The Usual Cost-Per-Click (CPC) on Google Ads
The average CPC on Google Ads varies based on factors such as industry, keywords, and location. On average, the CPC ranges from $1 to $2 on the Google Search Network. However, in highly competitive industries, it can go as high as $50 or more.
The Cost-Per-Click (CPC) on Google Ads can greatly influence digital marketing strategies. Understanding CPC variations across different industries, keywords, and locations is essential for optimizing advertising budgets and maximizing ROI. Below is an overview of the average CPC across various industries, along with factors affecting CPC.
| Industry | Average CPC | Highly Competitive CPC | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Legal | $6 - $15 | $50+ | High competition due to lucrative client acquisition. |
| Finance & Insurance | $3 - $12 | $30+ | Keywords related to loans and insurance can be particularly pricey. |
| Healthcare | $2 - $10 | $20+ | Terms related to specific treatments or medical professionals can drive costs up. |
| Technology & Software | $1 - $5 | $10+ | Emerging tech keywords can see spikes in CPC during product launches. |
| Education | $2 - $8 | $20+ | CPC can rise for degree programs and certifications. |
| E-commerce | $1 - $5 | $20+ | Seasonal trends can affect CPC, especially around holidays. |
| Real Estate | $1 - $5 | $10+ | Local targeting can influence costs significantly. |
| Travel & Hospitality | $1 - $4 | $15+ | Costs rise during peak travel seasons and special events. |
| Home Services | $2 - $7 | $15+ | Local service keywords, such as plumbing or roofing, can be highly competitive. |
| Automotive | $2 - $6 | $15+ | CPC can vary greatly based on specific car models and brands. |
Key Factors Influencing CPC
- Industry Competition: High-demand industries with lucrative customer acquisition often lead to higher CPCs. Legal and finance industries are prime examples where businesses are willing to pay more for leads.
- Keyword Selection: The specificity and intent behind keywords determine CPC. Long-tail keywords usually have lower competition and CPC compared to broad, high-traffic keywords.
- Geographic Location: CPC can vary significantly by location. Urban areas tend to have higher CPCs due to increased competition.
- Ad Quality and Relevance: Google rewards high-quality ads with lower CPCs through its Quality Score metric. Well-targeted, relevant ads can lead to lower costs.
- Seasonality: Certain times of the year, such as holidays or major events, can lead to fluctuations in CPC as demand for specific keywords increases.
- Bid Strategy: Manual bidding versus automated bidding strategies can also impact CPC, depending on how aggressively a business wants to compete for clicks.
Standard Cost-Per-Thousand Impressions (CPM) on Google Ads

CPM or cost-per-thousand impressions is another popular bidding strategy on Google Ads, particularly for display campaigns. Similar to CPC, the standard CPM varies based on factors like industry and location.
Key Insights on Standard CPM in Google Ads
- Understanding CPM: CPM stands for Cost-Per-Thousand Impressions. This bidding strategy allows advertisers to pay for ad impressions rather than clicks, making it ideal for brand awareness campaigns.
- Factors Influencing CPM:
- Industry Type: Certain industries have higher competition, leading to elevated CPM rates. For instance, finance and insurance sectors typically see higher CPM due to the value of leads.
- Geographic Location: CPM rates can vary significantly based on the target location. Urban areas may have higher CPMs due to greater competition and audience size.
- Ad Placement: Different placements (e.g., mobile vs. desktop, or specific websites within the Google Display Network) can influence costs.
- Seasonality: Certain times of the year (e.g., holidays, back-to-school season) can lead to spikes in CPM due to increased competition among advertisers.
- Targeting Options: More refined targeting options (demographics, interests, etc.) can also lead to higher CPMs as advertisers aim for a more specific audience.
3. Best Practices for Managing CPM:
- A/B Testing: Regularly test different ad creatives and placements to identify which combinations yield the best CPM and ROI.
- Audience Segmentation: Develop segmented audiences to optimize your bidding strategy and potentially lower your CPM.
- Monitor Competitor Activity: Keep an eye on competitor CPM trends in your industry to adjust your strategy accordingly.
Standard CPM Table
The following table provides an overview of the standard CPM ranges by industry. Note that these are indicative figures and can vary based on specific campaign parameters.
| Industry | Average CPM Range (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | $2.00 - $5.00 | High value due to patient acquisition costs. |
| Finance & Insurance | $3.00 - $6.00 | Competitive landscape with high lead value. |
| E-commerce | $1.50 - $4.00 | Varies based on product type and seasonality. |
| Technology | $2.00 - $4.50 | Higher CPM for niche tech products. |
| Travel & Hospitality | $1.50 - $3.50 | Seasonality impacts CPM during peak travel times. |
| Real Estate | $2.50 - $5.00 | High competition for listings. |
| Food & Beverage | $1.00 - $3.00 | Varied based on local competition. |
| Fashion & Apparel | $1.50 - $4.00 | Influencer impact can drive CPM higher. |
What is the Typical Cost-Per-Action (CPA) for Google Ads?
CPA or cost-per-action is a bidding strategy where you pay for each action a user takes on your website. The typical CPA for Google Ads can range from $2 to $30, depending on the industry and the action you're tracking.
Factors Influencing CPA
- Industry Competition: Highly competitive industries like finance or insurance tend to have higher CPAs due to increased bidding.
- Target Audience: The more niche or specific the audience, the higher the CPA may be, as advertisers compete for limited visibility.
Action Type: Different actions (like signing up for a newsletter vs. making a purchase) will have varying CPA associated with them.
- Quality Score: Google’s Quality Score affects how much you pay per click and can impact your CPA; better quality ads can lead to lower CPAs.
- Seasonality: Certain times of the year (like holidays) may lead to fluctuating CPAs, as demand increases.
Typical Cost-Per-Action (CPA) by Industry
| Industry | Typical CPA Range ($) | Common Actions Tracked |
|---|---|---|
| E-commerce | $10 - $30 | Purchase, Add to Cart |
| Finance/Insurance | $15 - $50 | Quote Request, Lead Form Submission |
| Travel & Hospitality | $5 - $25 | Booking, Inquiry Form Submission |
| Education | $10 - $40 | Course Enrollment, Information Request |
| Real Estate | $20 - $60 | Property Inquiry, Lead Submission |
| B2B Services | $30 - $100 | Demo Request, Contact Form Submission |
| Health & Wellness | $10 - $40 | Appointment Booking, Newsletter Sign-Up |
| Technology | $15 - $50 | Software Download, Free Trial Request |
| Automotive | $20 - $60 | Test Drive Request, Lead Generation |
Additional Insights
- E-commerce: Given the direct correlation between clicks and sales, e-commerce often sees a higher CPA due to the value of conversions.
- Finance/Insurance: These sectors are heavily regulated and typically involve high customer lifetime values, which can justify a higher CPA.
- Travel & Hospitality: With many potential touchpoints (like inquiries and bookings), CPAs can vary widely based on the specific action.
- Real Estate: The high value of real estate transactions can lead to higher CPAs, but successful campaigns can yield substantial ROI.
Average Click-Through Rate (CTR) on Google Ads
CTR or click-through rate is the ratio of users who click on your ad to the number of total users who viewed the ad. The average CTR on Google Ads is around 2%. However, a well-optimized ad can have a CTR as high as 4% or 5%.
Key Insights:
- The average CTR across Google Ads is approximately 2%.
- A well-optimized ad can achieve a CTR of 4% to 5% or higher, depending on the industry, targeting, and ad quality.
- Higher CTR indicates better ad relevance and effectiveness in engaging users.
Factors Influencing CTR
- Ad Relevance: Ensure ad copy aligns with user intent and keywords.
- Ad Position: Ads in higher positions tend to receive more clicks.
- Ad Extensions: Utilizing ad extensions (site links, callouts, structured snippets) can enhance visibility and CTR.
- Targeting: Precise targeting (demographics, location, interests) improves the likelihood of clicks.
- Creative Elements: Compelling headlines and engaging visuals can capture user attention effectively.
Average CTR by Industry
| Industry | Average CTR (%) | Well-Optimized CTR (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Retail | 2.48 | 4.00 |
| Travel | 1.90 | 3.80 |
| Finance & Insurance | 2.65 | 4.50 |
| Technology | 2.09 | 4.10 |
| Education | 3.09 | 5.20 |
| Healthcare | 3.36 | 5.00 |
| Real Estate | 2.25 | 4.00 |
| Automotive | 1.95 | 3.90 |
| Home Services | 2.50 | 4.00 |
| Entertainment | 2.76 | 4.25 |
Strategies to Improve CTR
- A/B Testing: Regularly test different ad copies and landing pages to identify what resonates best with your audience.
- Use of Keywords: Incorporate strong, relevant keywords in your headlines and descriptions to improve relevance and searchability.
- Compelling Call-to-Action (CTA): Use clear and enticing CTAs to encourage users to click.
- Mobile Optimization: Ensure ads are optimized for mobile devices, as a significant portion of searches comes from mobile users.
- Monitor and Adjust: Continuously track performance metrics and adjust strategies based on data insights.
- Utilize Remarketing: Target users who have previously interacted with your site to increase the likelihood of clicks.
Common Monthly Budget Allocations for Google Ads Management
When it comes to monthly budget allocations for Google Ads management, businesses usually spend around 10% to 20% of their total ad spend on management services. However, this can vary based on the complexity of the campaign and the level of service provided by the agency.
| Ad Spend Range | Management Fee % | Estimated Management Fee | Service Level | Complexity of Campaign |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| $1,000 - $5,000 | 15% | $150 - $750 | Basic management, monitoring, and reporting | Low complexity (single campaign, few keywords) |
| $5,001 - $10,000 | 12% | $600 - $1,200 | Intermediate management, A/B testing, and optimizations | Moderate complexity (multiple campaigns, varied keywords) |
| $10,001 - $20,000 | 10% | $1,000 - $2,000 | Advanced management, strategic planning, and detailed analytics | High complexity (diverse products, multiple audiences) |
| $20,001 - $50,000 | 8% | $1,600 - $4,000 | Premium management, extensive reporting, and custom strategies | Very high complexity (national campaigns, seasonal promotions) |
| $50,001+ | 5% | $2,500+ | Enterprise-level management, dedicated account teams, and comprehensive analysis | Extremely high complexity (global brands, extensive market research) |
Insights on Budget Allocations
- Service Levels: The level of service provided can greatly influence the management fee percentage. More complex campaigns typically require more hands-on management, which justifies higher fees.
- Campaign Complexity: The complexity of a campaign often correlates with the number of products or services advertised, the target demographics, and the overall marketing strategy. As a campaign becomes more complex, the need for strategic management increases.
- Flexibility: It's essential for businesses to remain flexible with their management fees based on performance. If an agency consistently drives high ROI, it may be worth considering a higher management fee.
- Performance-Based Models: Some agencies offer performance-based pricing models where the management fee is tied to the results achieved, such as conversion rates or revenue generated. This can incentivize agencies to optimize campaigns effectively.
- Regular Reviews: Businesses should conduct regular reviews of their Google Ads performance and management fees to ensure they align with overall marketing goals and ROI.
When planning your Google Ads budget, understanding how management fees fit into your overall ad spend is crucial. By considering the complexity of your campaigns and the level of service you need, you can allocate your budget in a way that maximizes performance and drives growth.
Strategizing Your Google Ads Budget: A Tutorial
Properly strategizing your Google Ads budget is crucial for achieving your advertising goals. This tutorial will guide you through the process of setting a realistic budget, choosing the right bidding strategies, and tracking your campaign performance.
Step 1: Define Your Goals
Before setting a budget, it’s essential to define your advertising goals. Are you looking to increase brand awareness, generate leads, or drive sales? Your goals will influence how you allocate your budget.
Step 2: Set a Realistic Budget
Your budget should be based on your advertising objectives, the lifetime value of your customers, and your overall marketing budget. Consider the following factors:
- Average Cost-Per-Click (CPC): Research the average CPC for your industry.
- Monthly Ad Spend: Determine how much you can afford to spend monthly.
- Return on Investment (ROI) Expectations: Set realistic ROI expectations based on historical data or industry benchmarks.
Step 3: Choose the Right Bidding Strategy
Selecting the appropriate bidding strategy is crucial for maximizing your budget. Here are some common bidding strategies:
| Bidding Strategy | Best For | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Manual CPC | Experienced advertisers | You set the maximum CPC for your keywords. Offers control but requires more management. |
| Enhanced CPC (ECPC) | General optimization | Automatically adjusts your manual bids to maximize conversions while staying within your budget. |
| Target CPA | Lead generation and conversions | Sets bids to help get as many conversions as possible at the target cost per acquisition. |
| Target ROAS | Revenue-focused campaigns | Automatically sets bids to maximize conversion value based on target return on ad spend. |
| Maximize Clicks | Traffic generation | Sets bids to get the most clicks within your budget. |
| Maximize Conversions | Conversion-driven campaigns | Automatically sets bids to get the most conversions within your budget. |
Step 4: Monitor and Adjust Your Campaign
Regularly monitor your campaign performance to ensure you're on track to meet your goals. Key metrics to watch include:
- Click-Through Rate (CTR)
- Conversion Rate
- Cost Per Acquisition (CPA)
- Return on Ad Spend (ROAS)
Step 5: Utilize Tools for Budget Management
Leverage tools such as Google Ads Budget Planner and Google Analytics to track and analyze your spending and performance metrics. This allows you to make data-driven decisions.
Sample Budget Allocation Table
Here’s a sample budget allocation table for a hypothetical campaign. Adjust the categories based on your specific goals and objectives.
| Category | Monthly Budget | Percentage of Total Budget | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Search Ads | $1,500 | 50% | Drive targeted traffic to your website |
| Display Ads | $600 | 20% | Increase brand awareness in relevant contexts |
| Remarketing | $400 | 13% | Re-engage previous visitors to boost conversions |
| Video Ads | $300 | 10% | Enhance engagement and storytelling |
| A/B Testing | $200 | 7% | Experiment with ad copies and landing pages |
| Total | $3,100 | 100% |
Deciphering Google Ads Bidding Strategies
Google Ads provide several bidding strategies for advertisers, including manual CPC, automated CPC, CPA, and CPM. Understanding these bidding strategies can help you optimize your ad spend and get the most out of your campaigns.
Google Ads offers a variety of bidding strategies to cater to different advertising goals. Understanding each strategy's nuances allows advertisers to optimize their ad spend effectively, ensuring better ROI. Below is a breakdown of common bidding strategies.
Bidding Strategies Table
| Bidding Strategy | Description | Use Case | Approx. Bidding Amount |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual CPC | Advertisers set their own maximum cost-per-click (CPC) bids. | Control over individual bids; ideal for experienced advertisers. | $0.10 - $5.00 per click (varies by industry) |
| Automated CPC | Google automatically adjusts bids to maximize clicks within your budget. | Less hands-on management; good for broad campaigns. | Varies based on budget and competition |
| Target CPA | Bids are set to achieve a target cost per acquisition (CPA). | Focus on conversions; ideal when you have historical conversion data. | $5.00 - $50.00 per conversion (varies) |
| Maximize Conversions | Automatically sets bids to get the most conversions within your budget. | Best for campaigns focused solely on driving conversions. | Varies; based on daily budget and goals |
| Target ROAS | Sets bids to achieve a target return on ad spend (ROAS). | Ideal for revenue-focused campaigns; requires tracking revenue per conversion. | Varies based on profit margins |
| CPM (Cost Per Thousand Impressions) | Advertisers pay for every 1,000 impressions served. | Good for brand awareness campaigns; less focus on clicks. | $1.00 - $20.00 per 1,000 impressions (varies) |
| vCPM (Viewable CPM) | Similar to CPM but focuses on viewable impressions. | Optimal for campaigns prioritizing brand visibility. | $1.00 - $15.00 per 1,000 viewable impressions (varies) |
| Maximize Clicks | Automatically sets bids to get the most clicks within budget. | Best for campaigns aimed at driving traffic. | Varies based on competition and market |
Key Considerations for Bidding Strategies
- Campaign Objectives: Align your bidding strategy with specific goals (e.g., brand awareness, lead generation, sales).
- Data Availability: Leveraging historical data can enhance the effectiveness of automated bidding options like Target CPA and Target ROAS.
- Budget Flexibility: Ensure your budget allows for the bidding strategy you choose; some strategies may require a higher daily budget for optimal results.
- Industry and Competition: Research average CPCs and CPMs in your industry to set realistic expectations and bids.
- Performance Monitoring: Regularly analyze campaign performance and adjust your bidding strategy based on results to maximize ROI.
The Benefits of Collaborating with a Google Ads Specialist or Agency
Collaborating with a Google Ads specialist or agency can provide several benefits. They have the expertise to manage your campaigns effectively, saving you time and effort. They can also offer strategic insights and recommendations to improve your ad performance and maximize your ROI.

Navigating the complexities of Google Ads pricing can be overwhelming. Whether you’re a seasoned advertiser or just starting, understanding the costs associated with Google Ads is crucial for optimizing your campaigns and maximizing your return on investment.
What’s holding you back from achieving your advertising goals? Contact us today to find out how we can help you succeed!
Share this post: